Lately there has been a variety of toy robot arms and other robotic devices available from electronics retailers for a reasonable price, and considering that they usually contain a couple of servos or DC motors - it's quite simple to modify them to work with an Arduino. This opens all sorts of fun and interesting possibilities, and one more scientific example of this has been demonstrated by Ben Greer.
With his example, Ben has used a toy robot arm, and after adding some extra hardware to monitor the position of the arm's components - the concept of inverse Kinematics has been used to calculate the exact position of the arm to allow for a more precise control. Ben explains the basic theory and also provides the maths and code to run some examples, as shown below:
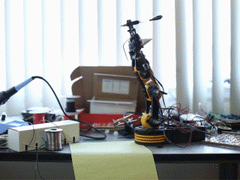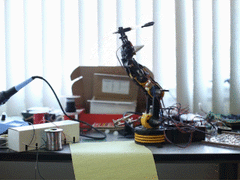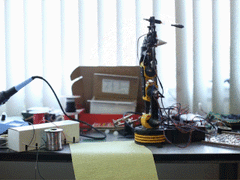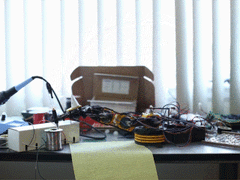
To read more about his fascinating hack, visit Ben's website. And for more, we're on twitter and Google+, so follow us for news and product updates as well.
If you're looking into controlling a pair of DC motors (or a stepper motor) from your Arduino or compatible, check out our new HBRIDGE: DC/stepper motor shield. Based around the powerful Allegro A4954 H-bridge driver IC you can control two DC motors with complete ease, or one bipolar stepper motor. With connections for external power management, a complete beginners' guide and documentation - motor control couldn't be any easier. For more information and to order, visit the HBRIDGE: page.











